How to Select the Right CMM Machine
In the world of accurate measurement, Coordinate Measuring Machines have become vitally important. These machines are highly capable of measuring the geometrical characteristics of a component accurately. This is used by multiple industries where precision is essential Like automotive, aerospace, medical and manufacturing, CMMs are Well-known measurement machines where accuracy is paramount.
However, Selecting the right CMM according to the measurement requirement will become very challenging without having proper knowledge. This blog will help you in find an appropriate CMM that matches your measurement requirements
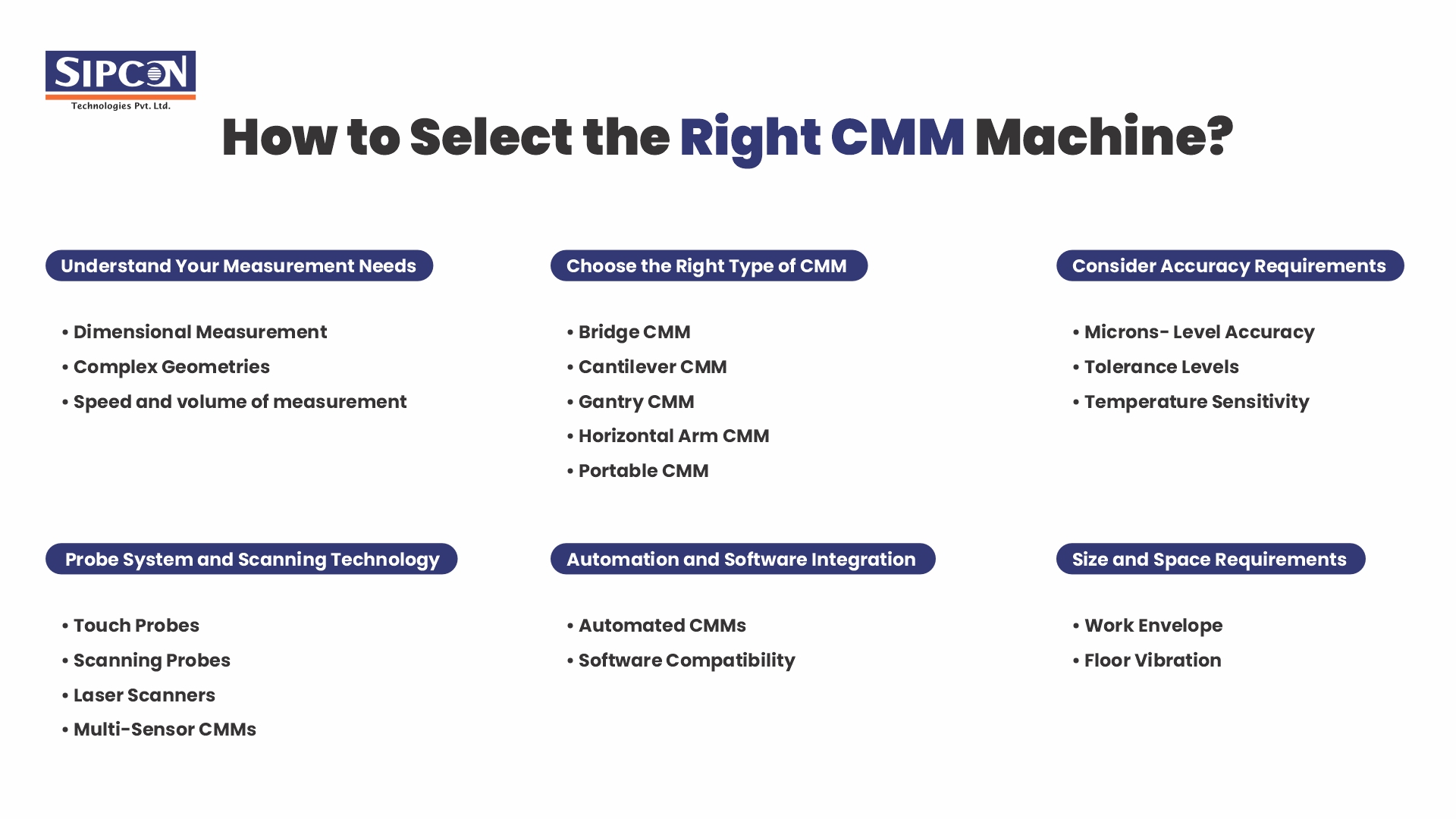
Understand Your Measurement Needs
The first step toward selecting the right CMM is to know what type of parts or components we must check. CMMs are used to Measure the multiple dimensions of an object with high accuracy.
- Dimensional Measurement: If Your main Requirement is to check dimensional measurement, understand the accuracy level needed for your components. Aerospace may require micron accuracy, whereas automotive components may tolerate slightly higher tolerances.
- Complex Geometries: If your components have complex physical geometries then CMM will be suitable as a measurement machine with advanced scanning capabilities, which can help in capturing highly detailed data.
- Speed and volume of measurement: Estimate the volume that must inspect so that you can know whether you require a CMM for inspection of a large volume or small volume. An automatic CMM measurement machine is designed for high production whereas manual or semi-manual are suitable for lower volume.
Choose the Right Type of CMM
Different types of CMMs are designed for specific measurement applications. Below are the primary types of CMMs
- Bridge CMM: These are the most common kinds of CMMs that are used in the measurement of components with high accuracy. It has a structure-like bridge that supports the measuring probe. Bridge CMMs are used for their ability to provide high precision in measurement.
- Cantilever CMM: Cantilever CMMs are like to bridge CMM, however they have single-column support. This is smaller in size as compared to the size of the bridge, ideal for measuring small to medium- sized components with high accuracy.
- Gantry CMM: These machines are generally designed for large, heavy parts like aerospace or shipbuilding components. This type of gantry CMM structure allows them to cover huge volumes.
- Horizontal Arm CMM: Just like its name, these machines come with a horizontal arm for measuring huge parts such as automotive bodies. They are suitable for the measurement of huge components without compromising with accuracy level.
- Portable CMM: Articulated arm CMMs offer mobility, offering you the components directly on the shop floor. They are mainly used for in-line inspections but sometimes fail to provide the accuracy level of fixed CMMs.
Consider Accuracy Requirements
Accuracy level is the most vital factor in selecting a CMM. The accuracy required for your parts plays an important role in choosing the right type and specifications of the CMM machine.
- Microns- Level Accuracy: Advanced and automatic CMMs offer measurement in micron level precision, which is important in industries like aerospace, medical devices, or advanced electronics.
- Tolerance Levels: If your components require tight tolerance, you need to use a measurement machine that can provide you with your desired level of accuracy consistently.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Remember that the accuracy of CMMs can be influenced by environmental conditions, especially temperature fluctuations. Look for machines with temperature compensation features if your facility experiences variable temperatures.
Probe System and Scanning Technology
The probe is an important element of the CMM and identifies how data is captured. There are many different types of probes and scanning technologies in the metrology industry.
- Touch Probes: This type of probe is most commonly in use by multiple industries, suitable for basic dimensional measurement tasks. The probe measures the component by touching the surface to capture the points for measurements.
- Scanning Probes: This Probe is used to measure complex geometrics and allow for the continuous scanning of a component’s surface to capture a huge amount of data for detailed measurement.
- Laser Scanners: These are most suitable for non-contact measurement especially the in case of soft or fragile parts Because they could be damaged by the physical touch of probe and show wrong results. Laser scanners are highly fast and high-density data capturing.
- Multi-Sensor CMMs: This probe comes with combining different sensor technologies, allowing users to use both touch and non-contact measurements in the same machine.
Automation and Software Integration
- Automated CMMs: These types of machines can be installed into the whole production lines to get real time measurement inspection, which reduces downtime and speeds up the production and quality control process.
- Software Compatibility: Check that the CMM software is compatible with your existing CAD OR CAM systems.
Size and Space Requirements
- Work Envelope: Select a measurement machine which matches the requirement of the size of the parts you are measuring. This is vital to balance the size of the machine with its accuracy without compromising performance.
- Floor Vibration: Some kinds of CMMs are sensitive to floor vibration which affects the measurement accuracy and shows variation in results. If your location has high vibrations, you must spend it on vibration isolation systems.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate CMM is an important decision as CMMs are very expensive and the right selection of CMM type on understanding your measurement requirements, what kinds of components or parts you will measure, and the accuracy and tolerance level. By considering the above-mentioned factors such as accuracy level, automation, space requirements and probe systems, choose a CMM that will enhance your production quality control processes.