Carbon Black Dispersion Measurement of Electrical Cables
Carbon black dispersion measurement is a crucial aspect of cable manufacturing as it affects the mechanical and electrical properties of the cable. Carbon black is used as a filler in cable insulation and sheathing to improve its toughness, electrical conductivity, and resistance to heat and chemicals. The uniform dispersion of carbon black particles in the polymer matrix is essential to ensure consistent and optimal cable performance.
Carbon black dispersion in cables can be measured using several methods, including light scattering, microscopy, and conductivity testing. Light scattering involves shining a light on the cable and measuring the amount of light scattered in different directions, indicating the degree of dispersion of the carbon black particles. Microscopy involves looking at a sample of the cable under a microscope to visually inspect the dispersion of the carbon black particles. Conductivity testing involves measuring the electrical conductivity of the cable, which can also indicate the degree of dispersion of the carbon black particles.
The Microscope measurement method is advantageous over other ways, such as light scattering or electrical conductivity measurements, as it provides a more direct and accurate measure of the carbon black dispersion. Light scattering methods provide only indirect information about the dispersion and can be influenced by other factors, such as the refractive index of the polymer matrix. Electrical conductivity measurements only provide information about the material’s conductivity and do not directly measure the dispersion of the carbon black particles.
The Microscope measurement method is considered to be the best method to measure carbon black dispersion as it provides direct and visual observation of the carbon black particles in the polymer matrix. This method involves observing a sample of the cable material under a microscope and analyzing the distribution of the carbon black particles. The microscope provides a magnified sample image, allowing a more detailed analysis of the dispersion pattern.
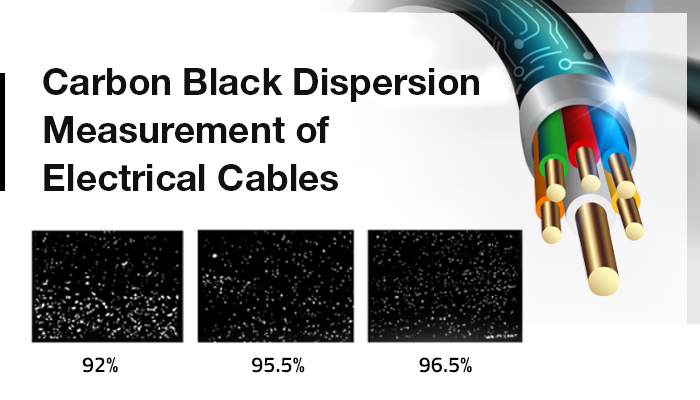
Carbon black dispersion in cables using a microscope
When using microscopy to measure carbon black dispersion in cables, a sample of the cable is taken and prepared for the examination. This typically involves cutting the cable at a specific angle to expose the cross-section and then mounting the sample on a slide for observation.
Under a microscope, the degree of dispersion of the carbon black particles can be evaluated by analyzing the distribution and size of the particles in the cross-section. A well-dispersed sample will have small and evenly distributed carbon black particles throughout the cable, while a poorly dispersed sample will have larger clusters of carbon black particles.
The method of measuring carbon black dispersion in cables using microscopy can be a precise and accurate way to evaluate the cable’s quality and optimize the manufacturing process.
In conclusion, carbon black dispersion measurement is important in cables as it affects the mechanical and electrical properties of the cable. The Microscope measurement method is considered to be the best method to measure carbon black dispersion as it provides a direct and visual observation of the carbon black particles in the polymer matrix, providing a more accurate and detailed analysis of the dispersion pattern.